Got some feedback and suggestions over last couple of weeks like “Could you please start basis before going machine learning!” and “Could you please talk about ecosystem where can do hands-on!” and another suggestion was “Could you please explain AWS and google cloud services and ecosystem!”….etc
In this note going talk about AWS ecosystem and services then move to Google cloud ecosystem and its services.
Global Infrastructure – AWS are hosted in multiple geographic world wide. Amazon provides the ability to place resources and data in multiple locations to improve performance, provide fault tolerance, high availability and cost optimization.
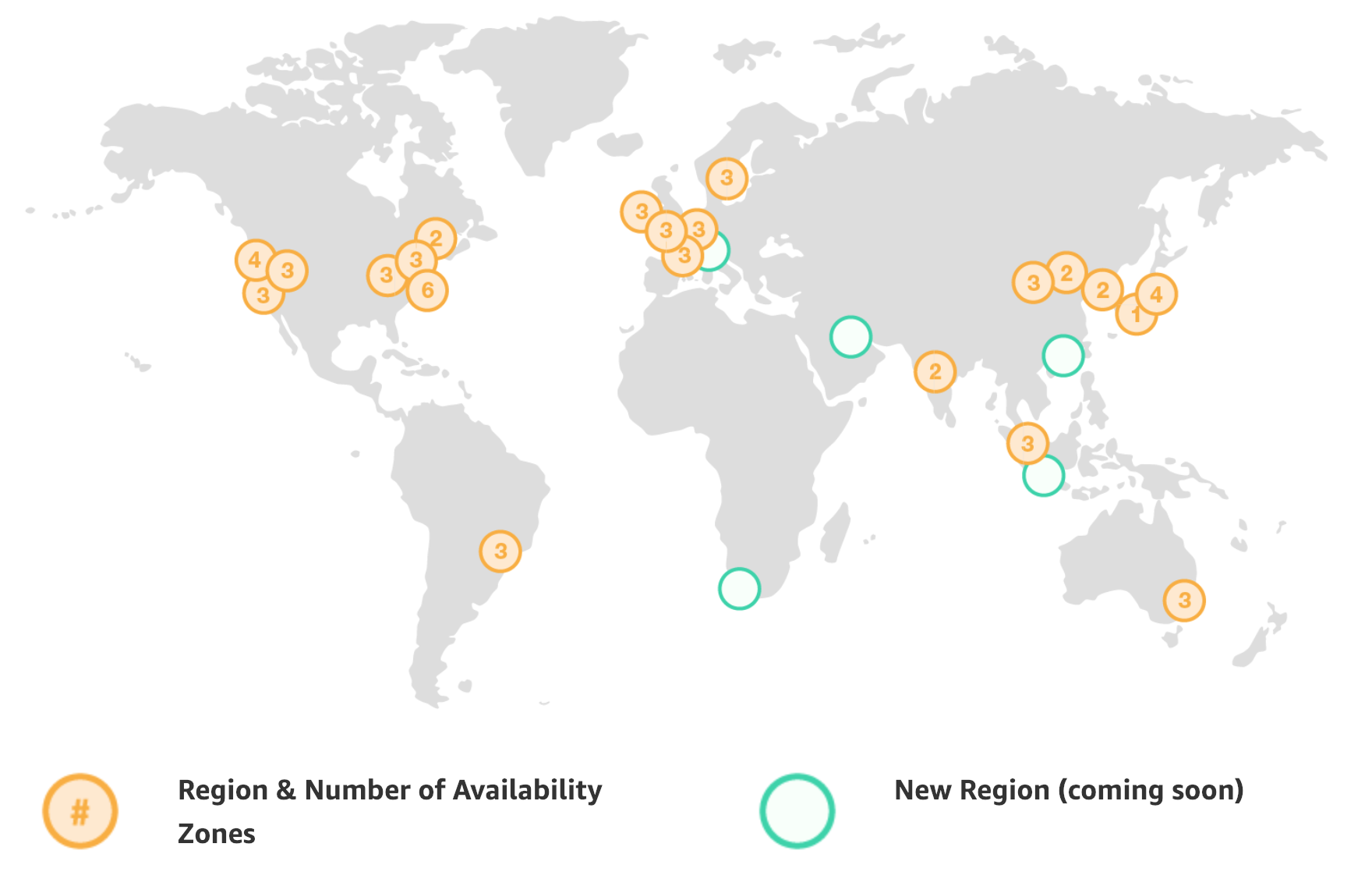
Regions (5) and Availability Zone (15) coming in 2019
What is Regions and Availability Zone?
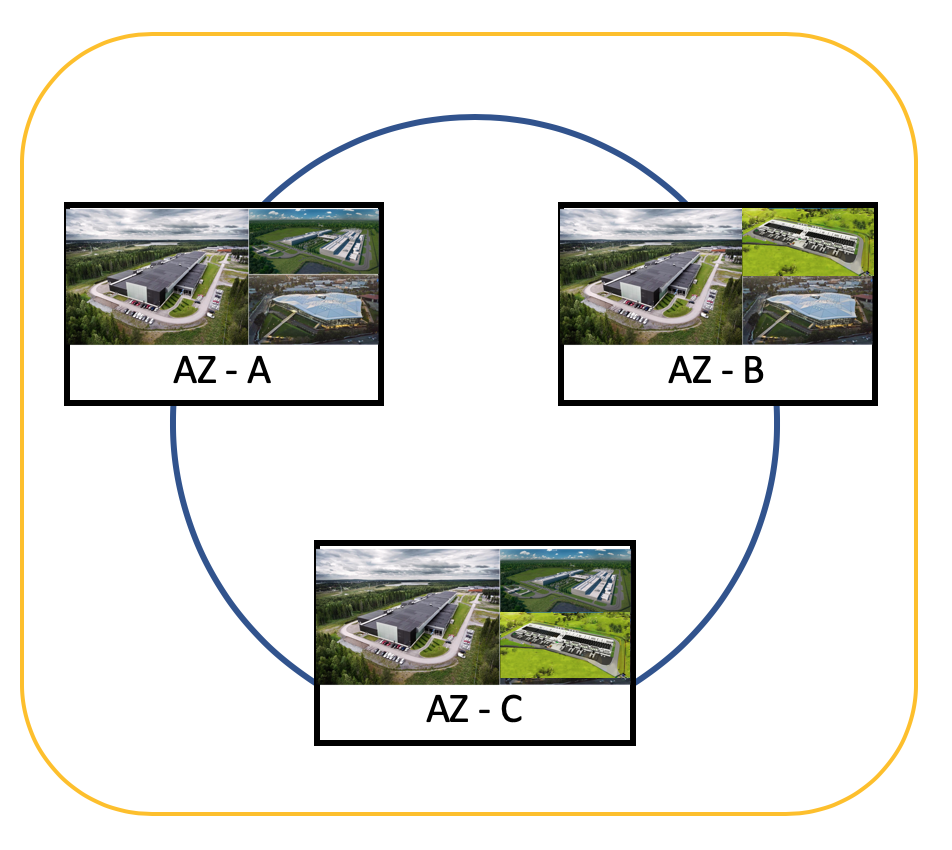
Availability Zone – Think like AZ as a Data Center, Data center is physical building with services and VPN, VPS and all required networking for cloud computing.

An availability might be several data centers because they are close together and connected with private and secure redundant low-latency network this is counted as 1 Availability Zone.

- Each AZ is physically isolated from each other so that an uncommon disaster such as fire, earthquake would only affect a single AZ
- AZs are geographically separated from each other, within the same region, and acts as an independent failure zone
- AZs are redundantly connected to multiple tier-1 transit providers
- AZs in a region are connected with low-latency private links and not through public internet
- Multi-AZ, distribution of resources across multiple Availability Zones, feature can be used to distribute instances across multiple AZ to provide High Availability
- AWS ensures that resources are distributed across the Availability Zones for a region by independently mapping Availability Zones to identifiers for each account. for e.g. us-east-1 region with us-east-1a AZ might not be the same location as us-east-1a AZ for another account. There’s no way for you to coordinate Availability Zones between accounts.
Regions – is a geographical area and consists more than 2 AZs. AWS provides customers with the flexibility to place instances and store data within multiple geographic regions called Region. Each region is an independent collection of AWS resources in a defined geography.
- Each region is a separate geographic area and is completely independent
- Each region is designed to be completely isolated from the other regions & helps achieve the greatest possible fault tolerance and stability
- Communication between regions is across the public Internet and appropriate measures should be taken to protect the data using encryption
- Data transfer between regions is charged at the Internet data transfer rate for both the sending and the receiving instance
- Resources aren’t replicated across regions unless done explicitly
Selection of a Region can be driven from a lot of factors
- Latency – Regions can be selected to be closet to the targeted user base to reduce data latency
- Cost – AWS provides the same set of services across all regions, usually, however the cost would differ from region to region depending upon the cost (due to land, electricity, bandwidth etc) incurred by Amazon and hence can be cheaper in one region compared to the other
- Legal Compliance – Lot of the countries enforce compliance and regulatory requirements for data to reside within the region itself
- Features – As not all the regions provide all the AWS features and services, the region selection can depend on the Services supported by the region
Edge Locations (150) – are endpoints for AWS which use for caching content.
- Edge locations are locations maintained by AWS through a worldwide network of data centers for the distribution of content.
- These locations are located in most of the major cities around the world and are used by CloudFront (CDN) to distribute content to end user to reduce latency.
AWS – High Level Services

will talk about couple of popular AWS services in this notes. starting with Security, Identify & Compliance.

Identity Access Management (IAM) – Using IAM, you can manage user and their level of access to AWS console, It is most important service to prevent unauthorised access and features are
- Centralised control of AWS account
- Shared Access to AWS account
- Granular Permisions
- Identity Federation
- Multi-factor Authentication
- provide temporary access for users/devices and services where required
- allows to setup own password rotation policy
- integrates with many different AWS services
- Support PCI DSS compliance in-case if you are taking credit card info …etc
IAM Key terms –
- Users – End users such as people, employees of an organisations…etc
- Groups – A collection of users, each user in the group will inherit the group’s permissions.
- Polices – polices are made of documents called police documents.
- Roles – Create roles and assign to AWS resources.
Key Points –
- IAM is universal, It is does not apply to regions at this time.
- The “root account” is simply account created when first setup the AWS account and it has full access.
- New user has “No permissions” when first created.
- New user has assigned “Access Key ID” and “Secret Access Keys” when first created.
- These are not the first

Simple Storage Service (S3) – Amazon Web Services (AWS) that provides object storage through a web service interface. Amazon S3 uses the same scalable storage infrastructure that Amazon.com uses to run its global e-commerce network.
- S3 is a safe, secure and storage
- It is Object-based storage – allow to upload files with following attributes
- Key (name of object)
- Value (data means sequence of bytes)
- Version ID (it is file versioning)
- Metadata (Data about data this is store)
- Subresource
- ACL – Access Control List
- Torrent
- The data is spread across multiple devices and facilities.
- Files can be from 0 bytes to 5 TB.
- S3 is unlimited storage.
- Files are store in Bucket.
- S3 is a universal namespace, so it must be unique i.e. https://s3.us-north.1.amazonaws.com/arsnotes
- S3 Read after Write constancy for PUTS new objects
- Eventual constancy for override PUTS and DELETES
- S3 has following guarantees
- 99.9% Availability
- 99.99999999999% durability (11 times 9’s)
S3 features
- S3 has Tiered storage
- Life Cycle Management for the Object to move other S3 Tier
- Versioning
- Encryption –
- In Transit if used SSL/TLS
- Server Side – Amazon will manage encryption keys
- S3 Managed Keys – SSE-S3
- AWS Key management Service, Managed Keys – SSE-KMS
- Service Side Encryption with customer provided Keys – SSE-C
- Client Side
- Customer encrypt the data before uploading on S3
- MFA Delete – to protect delete an object by accident
- Security – Using ACL and Bucket Policies
S3 Classes
- S3 Standard
- 99.9% Availability
- 99.99999999999% durability (9s x 11 times) and redundancy across multiple device and facilities and it is designed to sustain the loss from 2 facilities concurrently.
- S3 IA – Infrequent Access – For the data less infrequently access but requires rapid access when needed. cost is lower than S3 but charged a retrieval fee.
- S3 One Zone – IA – for lower-cost option for infrequently access data without multiple availability zone.
- S3 Intelligent Tiering – Designed to optimise the costs by automatically moving data to most cost-effecting access tier without performance impact and operational overhead based on data access/usage – it is machine learning based alogos
- S3 Glacier – Amazon S3 Glacier is a secure, durable, and extremely low-cost cloud storage service for data archiving and long-term backup but retrieval time is configurable from mins to hours.
- S3 Glacier Deep Archive –S3 Glacier Deep Archive is a new Amazon S3 storage class that provides secure, durable object storage for long-term data retention and digital but retrieval time is 12 hours,
S3 comparison
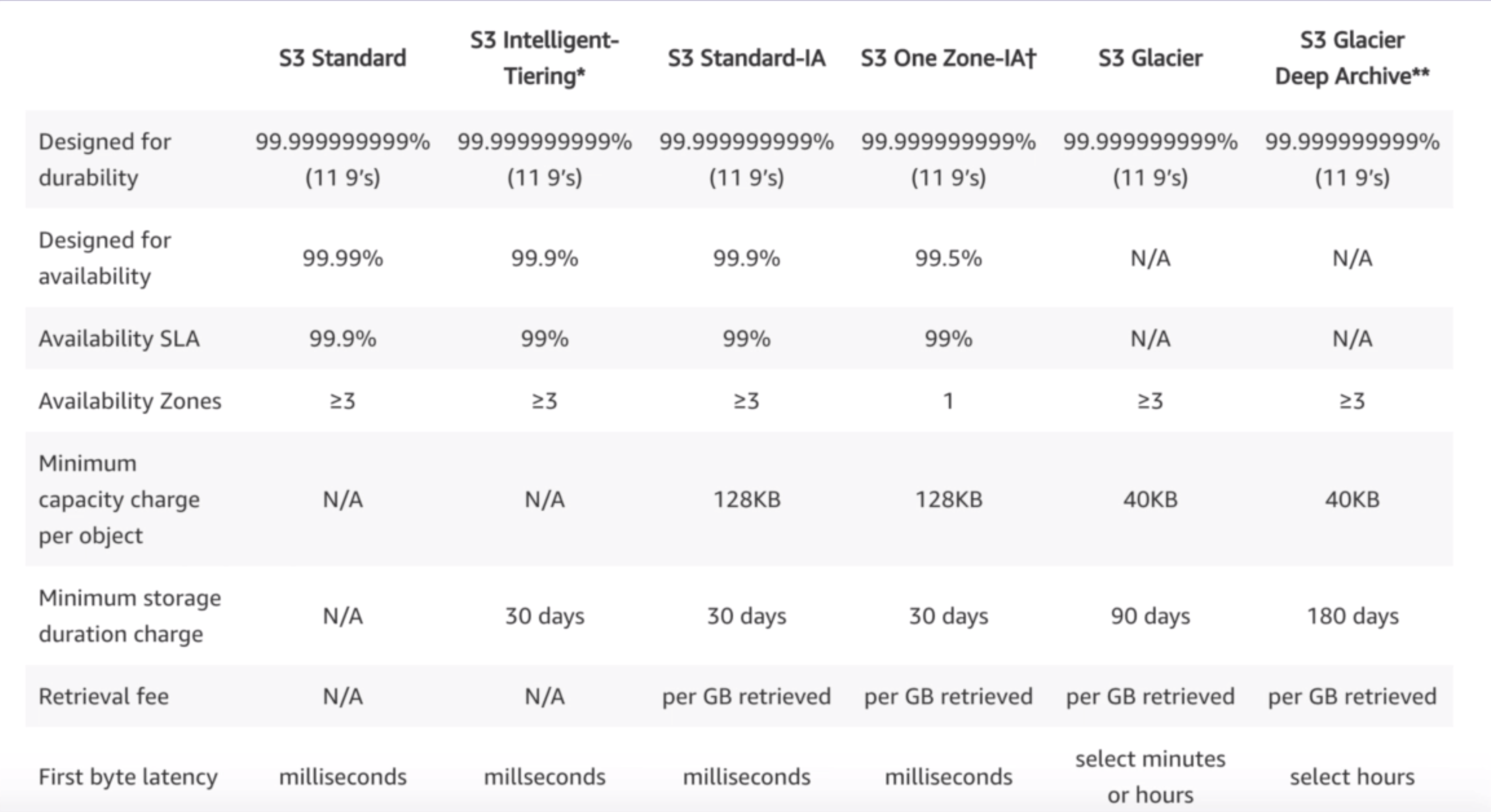
S3 Charges
S3 charges are based on following components
- Storage
- Request
- Storage Management pricing
- Data Transfer pricing
- Transfer Acceleration pricing – Pricing is based on the AWS edge location (AWS CloudFront Edge Network) used to accelerate transfer. S3 Transfer Acceleration pricing is in addition to Data Transfer pricing.
- Cross-Region Replication pricing – CRR is an Amazon S3 feature that automatically replicates data across AWS Regions. With CRR, every object uploaded to an S3 source bucket is automatically replicated to a destination bucket in a different AWS Region that you choose.
- AWS GovCloud Region – AWS GovCloud is an AWS Region designed to allow US government agencies and contractors to move more sensitive workloads into the cloud by addressing their specific regulatory and compliance requirements.
CloudFront
AWS cloudFront is a content delivery network (CDN), CDN is a distributed servers network that delivers webpages and other web content to the user based on user’s geographic locations, and the origin of the webpage call content delivery network server or CDNS.
Snowball
Snowball is a petabyte-scale data transport solution that uses devices designed to be secure to transfer large amounts of data into and out of the AWS Cloud. Using Snowball addresses common challenges with large-scale data transfers including high network costs, long transfer times, and security concerns. Customers today use Snowball to migrate analytics data, genomics data, video libraries, image repositories, backups, and to archive part of data center shutdowns, tape replacement or application migration projects. Transferring data with Snowball is simple, fast, more secure, and can be as little as one-fifth the cost of transferring data via high-speed Internet.
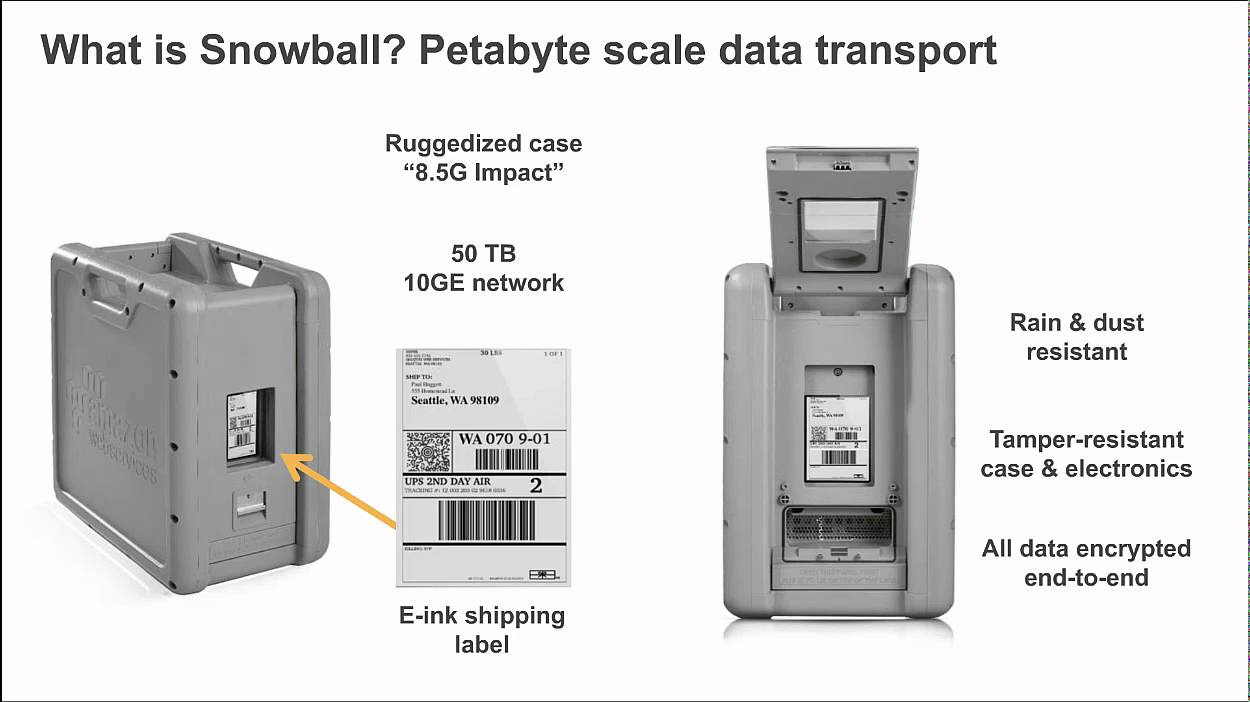
Snowball comes in either 50TB or 80TB, Snowball uses multiple layers of security to secure the data including tamper-resistant seals and includes a built-in Trusted Platform Module (TPM) that uses a dedicated processor designed to detect any unauthorized modifications to the hardware, firmware, or software. AWS inspects every device for any signs of tampering and to verify that no changes were detected by the TPM.
All data transferred to Snowball is automatically encrypted with 256-bit encryption keys that you can manage by using the AWS Key Management Service (KMS). The encryption keys are never sent to, or stored on the device, to help ensure your data stays secure during transit.
Snowball edge
Snowball Edge Storage Optimized provides 100 TB of capacity and 24 vCPUs and is well suited for local storage and large scale data transfer.
Snowball Edge Compute Optimized provides 52 vCPUs and an optional GPU for use cases such as advanced machine learning and full motion video analysis in disconnected environments.
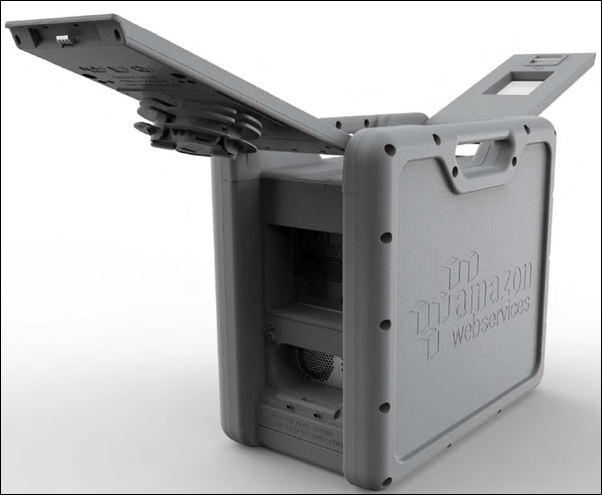
Snowball Edge devices use tamper-evident enclosures, 256-bit encryption, and industry-standard Trusted Platform Modules (TPM) designed to ensure both security and full chain-of-custody for your data. Encryption keys are managed with the AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and they are never stored on the device.
Snowball Mobile
AWS Snowmobile is an Exabyte-scale data transfer service used to move extremely large amounts of data to AWS. You can transfer up to 100PB per Snowmobile, a 45-foot long ruggedized shipping container, pulled by a semi-trailer truck. Snowmobile makes it easy to move massive volumes of data to the cloud, including video libraries, image repositories, or even a complete data center migration. Transferring data with Snowmobile is more secure, fast and cost effective.

Snowball comparison

Storage Gateway
AWS Storage Gateway is a hybrid storage service that enables on-premises applications to seamlessly use AWS cloud storage.
AWS Storage Gateway’s software appliance is available to download as VM images that can be installed in Datacenter. AWS Storage Gateway supports VMware SCSI or Microsoft Hyper-V and activate it using AWS console.
Storage Gateway Type
File Gateway (NFS) – File objects are store in S3 buckets using NFS mount points.
Volume Gateway (iSCSI) – the volume interface presents applications with disk volumes using iSCSI block protocols.
- Stored Volumes – Entire dataset store onsite but async backed up to S3.
- Cached Volumes – Entire dataset store S3 and the most frequently accessed data is cached onsite.
- Tap Gateway – It is offer a durable, cost-effective solution to achieve data in AWS cloud.

Elastic Compute Cloud –Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It is designed to make web-scale cloud computing easier for developers. Amazon EC2’s simple web service interface allows to obtain and configure capacity with minimal friction.
EC2 reduces the time obtained and boot new server instance in a minutes and allowing quickly scale capacity, both ways up and down based on computing requirements changed.
EC2 pricing models –
- OnDemand – Pay as you go
- Reserved – Pay for 1 to 3 years with minimum and better cost
- Spot – Bid for a price
- Dedicated Host – not shared with multi-tenant like Gov or healthcare.
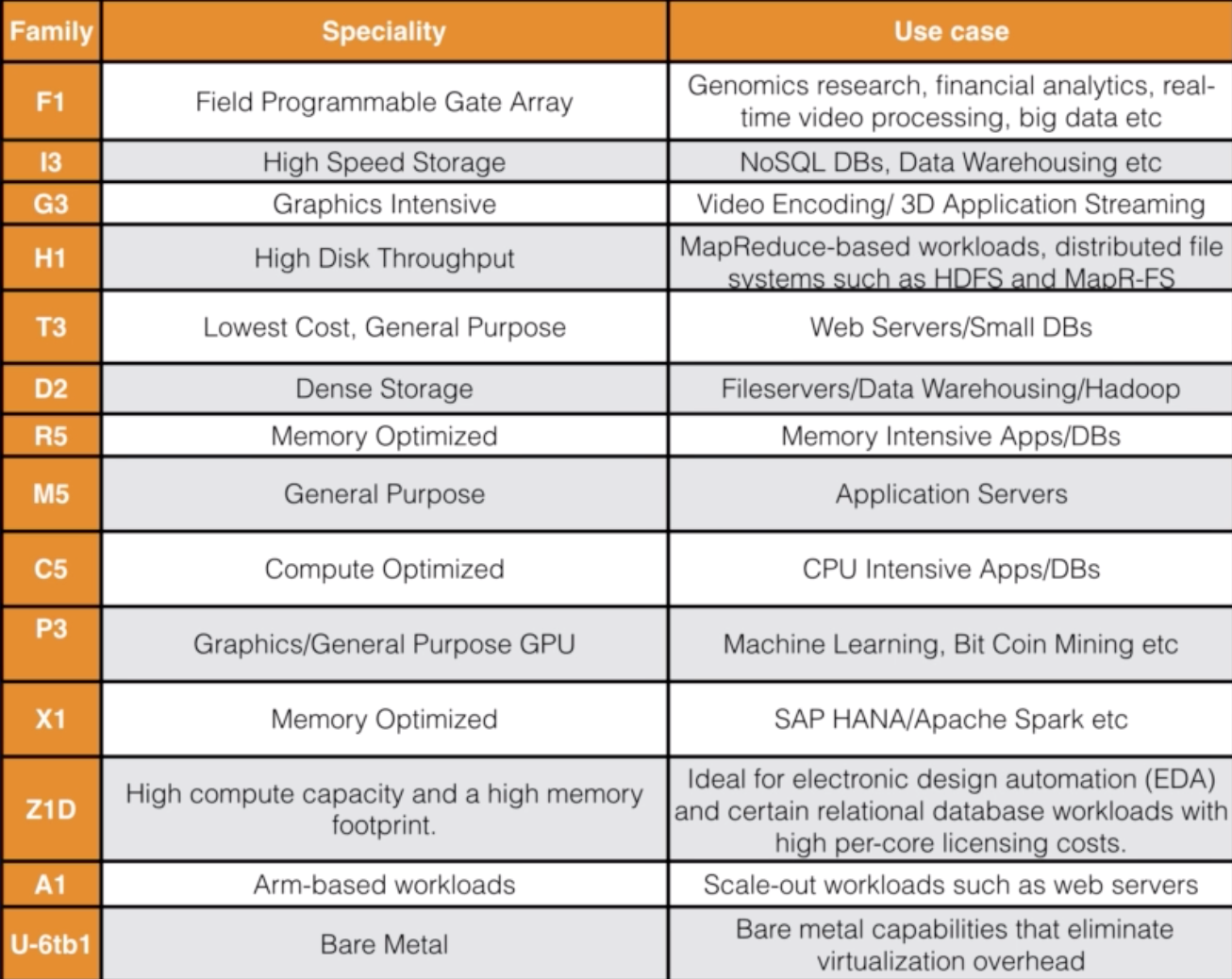
EC2 Instances Type –
Leave a comment